Health Benefits of Pinto Beans
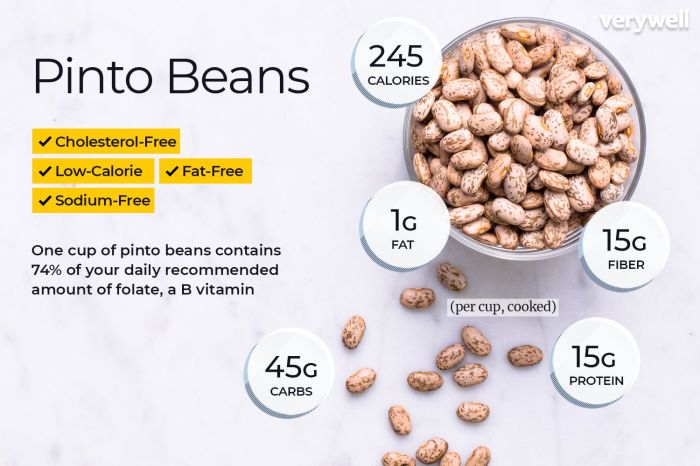
Pinto beans nutrition facts – Pinto beans, a staple in many cuisines, offer a wealth of nutritional benefits that contribute to overall health and well-being. Their high fiber content, coupled with an impressive array of vitamins and minerals, makes them a powerful addition to a balanced diet. This section will explore the evidence-based health advantages of incorporating pinto beans into your regular meals, alongside a discussion of potential risks associated with excessive consumption and a sample meal plan to illustrate their culinary versatility.
Impact on Heart Health
Pinto beans are a significant source of soluble fiber, which plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health. Soluble fiber helps lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive tract and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. Studies have shown a correlation between increased fiber intake and a reduced risk of heart disease. Furthermore, pinto beans are rich in potassium, a mineral that helps regulate blood pressure.
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is essential for preventing heart disease and stroke. The combination of soluble fiber and potassium in pinto beans contributes significantly to their heart-protective properties. For example, a study published in the
Journal of the American Heart Association* found that individuals who consumed diets rich in legumes, including pinto beans, experienced a statistically significant decrease in their risk of cardiovascular events.
Contribution to Weight Management, Pinto beans nutrition facts
The high fiber and protein content of pinto beans contributes to feelings of fullness and satiety, aiding in weight management. Fiber absorbs water in the digestive system, increasing its volume and promoting a feeling of being full, which can help reduce overall calorie intake. Protein also plays a crucial role in satiety, helping to regulate appetite and prevent overeating.
Moreover, pinto beans are relatively low in calories compared to many other protein sources, making them a weight-management-friendly food. A diet incorporating pinto beans as a regular source of protein and fiber can support healthy weight loss or maintenance. For instance, replacing processed foods high in unhealthy fats and sugars with pinto beans can lead to a significant reduction in daily caloric intake, contributing to weight loss over time.
Role in Blood Sugar Control
Pinto beans possess a low glycemic index (GI), meaning they cause a slow and gradual rise in blood sugar levels after consumption. This is largely due to their high fiber content, which slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing type 2 diabetes and managing existing conditions. The slow release of glucose from pinto beans prevents the sharp spikes in blood sugar that can occur after consuming high-GI foods.
This makes them a beneficial addition to the diets of individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the disease. Studies have demonstrated the positive impact of high-fiber, low-GI foods like pinto beans on improving insulin sensitivity and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Potential Risks of Excessive Consumption
While pinto beans offer numerous health benefits, excessive consumption can lead to some negative effects. The high fiber content, while beneficial in moderation, can cause digestive discomfort, including gas, bloating, and flatulence, in some individuals. Furthermore, pinto beans contain antinutrients, such as phytic acid, which can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals. However, these antinutrients are largely mitigated through proper cooking methods, such as soaking and sprouting.
It’s advisable to gradually increase pinto bean intake to allow the digestive system to adapt.
Sample Meal Plan Incorporating Pinto Beans
Pinto beans are remarkably versatile and can be incorporated into a wide range of dishes. A sample meal plan showcasing their versatility might include:Breakfast: A hearty bowl of pinto bean and vegetable chili.Lunch: A simple salad with pinto beans, corn, avocado, and a lime vinaigrette.Dinner: Black bean and pinto bean burritos with brown rice and salsa.Snacks: A small bowl of pinto beans seasoned with chili powder and lime juice.This sample meal plan demonstrates how easily pinto beans can be integrated into a healthy and balanced diet, providing a variety of flavors and textures.
Pinto Beans and Dietary Considerations: Pinto Beans Nutrition Facts

Pinto beans, while nutritious, require careful consideration for individuals with specific dietary needs or health conditions. Their high fiber content, carbohydrate makeup, and potential interactions with certain medications necessitate a mindful approach to their inclusion in various diets. Understanding these considerations is crucial for maximizing the benefits of pinto beans while minimizing potential risks.Pinto beans and specific dietary needs present a complex interplay.
Their nutritional profile, while beneficial for many, requires careful management in certain situations.
Pinto Beans and Diabetes Management
Individuals with diabetes need to carefully monitor their carbohydrate intake. Pinto beans are relatively high in carbohydrates, which can impact blood sugar levels. However, their high fiber content helps slow down the absorption of sugars, mitigating the sharp spikes in blood glucose often associated with high-carbohydrate foods. Careful portion control and mindful integration into a balanced meal plan, potentially alongside other low-glycemic foods, are key to managing blood sugar levels effectively while enjoying the benefits of pinto beans.
Consulting a doctor or registered dietitian is recommended to determine the appropriate serving size and integration strategy for individual diabetic needs.
Pinto Beans and Blood Pressure
Pinto beans’ high potassium content contributes to healthy blood pressure management. Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body, reducing strain on the cardiovascular system. However, individuals with kidney problems should exercise caution, as excessive potassium intake can be problematic. For those with high blood pressure, including pinto beans as part of a balanced diet that is also low in sodium can be beneficial, but individual needs and potential interactions with other medications should always be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Pinto Beans and Digestive Health
The high fiber content in pinto beans, while generally beneficial for digestive regularity, can also cause digestive discomfort for some individuals, especially those with sensitive digestive systems. Bloating, gas, and flatulence are common side effects of consuming large quantities of beans. Soaking and cooking pinto beans thoroughly can help reduce these issues by breaking down some of the complex carbohydrates that contribute to gas production.
Gradually increasing the amount of pinto beans consumed allows the gut microbiome to adjust, minimizing digestive distress. For those with severe digestive issues, consulting a doctor or registered dietitian is advised.
Pinto Bean Interactions with Medications
Pinto beans, like other legumes, contain compounds that can interact with certain medications. For example, some medications used to treat Parkinson’s disease may interact with levodopa, and the consumption of pinto beans could potentially affect the medication’s effectiveness. Furthermore, the high fiber content in pinto beans might interfere with the absorption of some medications. It’s crucial for individuals on medication to consult their doctor or pharmacist about potential interactions before significantly altering their diet to include pinto beans.
Pinto Bean Allergies and Intolerances
Although relatively rare, allergies and intolerances to pinto beans do exist. These reactions can range from mild digestive discomfort to more severe allergic reactions such as hives, itching, swelling, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis. Individuals with known legume allergies should exercise extreme caution and avoid consuming pinto beans entirely. If any allergic symptoms develop after consuming pinto beans, immediate medical attention should be sought.
It’s important to note that a sensitivity to one type of legume does not automatically indicate sensitivity to all legumes, but caution is warranted.
Detailed FAQs
Are pinto beans good for weight loss?
Their high fiber content promotes satiety, helping manage appetite and potentially aiding weight management efforts. However, portion control remains crucial.
Can I eat pinto beans every day?
While generally healthy, daily consumption might lead to digestive discomfort for some due to their high fiber content. Moderation is key.
Do pinto beans cause gas?
Yes, the high fiber content can contribute to gas and bloating in some individuals. Soaking and proper cooking methods can help mitigate this.
Are canned pinto beans as nutritious as dried?
Canned pinto beans are convenient but may contain added sodium. Dried beans, when properly prepared, generally retain more nutrients.
How long can I store cooked pinto beans?
Store cooked pinto beans in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 4 days. Freezing extends their shelf life significantly.